Bnibling/Acoustic Lab
From Physiki
Harmonics
Barrett Nibling
December 4th, 2007
Contents |
Abstract
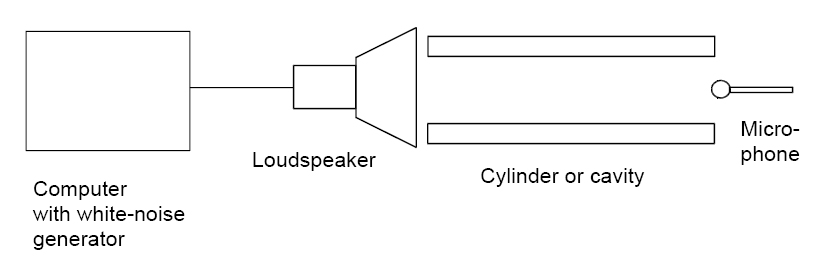
This experiment dealt with the unique frequency patterns, known as harmonics, that sound produces in a resonator. Using white noise generated by a computer and transmitted through a speaker into our resonant cavity, a pipe, and at the other end was placed a microphone to record the outgoing frequencies. Using the geometry of the pipe and derived equations, theoretical values were calculated were calculated and compared to the measured values. The experimental data was within <insert %>% of the theoretical data.
List of Figures
Introduction
Theory
Procedure
Results
| Color | θdiff (degrees) | λ (nm) | Error (nm) | Published λ (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purple | 15.6 | 448.0 | 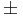 2.0 2.0
|
447.148 | |
| Teal | 16.4 | 470.3 | 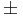 2.0 2.0
|
471.314 | |
| Green | 17.2 | 492.6 | 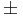 2.0 2.0
|
492.193 | |
| Green | 17.5 | 500.9 | 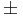 2.0 2.0
|
501.567 | |
| Yellow//Orange | 20.7 | 588.8 | 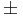 2.0 2.0
|
587.562 | |
| Red | 23.6 | 666.9 | 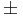 2.0 2.0
|
667.815 | |
| Dim Red | 25.1 | 706.7 | 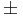 1.9 1.9
|
??? |
Error Analysis
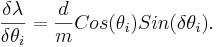
Then the total error is the sum of the two partial derivatives added in quadrature,
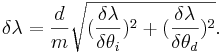
Conclusion
References
[1]
[2]