Week of 9/4
Try the following notebook
| |
Also, take a look at Mathematica Tips and Tricks.
A real amplitude and phase measurement. Top figure shows the amplitude of the transmitted and reflected electric fields. Bottom are the corresponding amplitudes. Click to download the annotated pdf.
| |
when is it ok to assume physical expressions are complex?
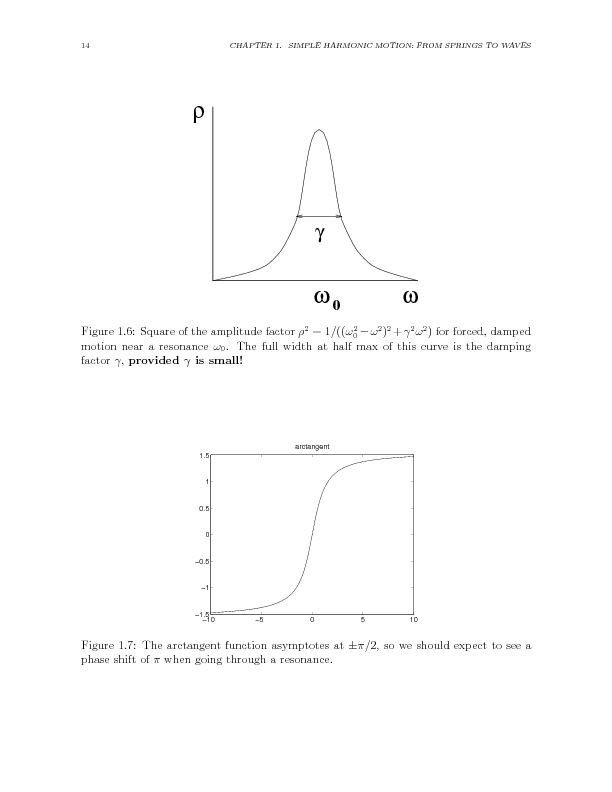
Consider the forced, damped, simple harmonic oscillator.
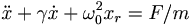
Let's pretend that both x and F are actually complex variables. So we would write
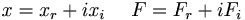
Plugging these into the equation above we get
![\ddot{x_r} + \gamma \dot{x_r} + \omega_0 ^2 x_r +
i\left[\ddot{x_i} + \gamma \dot{x_i} + \omega_0 ^2 x_i\right] = F_r/m + i F_i /m](/csm/wiki/images/math/2/0/0/200ca3de1b5126a171fd0ec143de9e02.png)
Now, whenever you have a complex equation this is equivalent to two real equations, among the real parts and the imaginary parts. Here we have
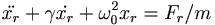
and
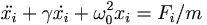
Now the trick is to solving real physical problems (at least linear ones) is to throw away the imaginary part.
Brief Digression on operators.
| |